Plant Tissue Culture
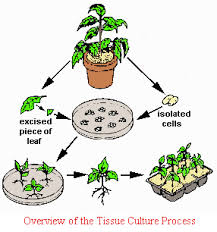
The process by which desirable plants can be grown from any plants part,tissue or cells artificially in the laboratory in an artificially prepared nutrient medium under aseptic condition is known as plant tissue culture.
Historical background of tissue culture:
Haberlandt(1896) was the first person to culture isolated vegetative cells.He was able to maintain the cell in the medium but failed to differentiate it.In 1934 different worker P.R. white,R.s Gautherate and P.Hobegurt were able to grow cambium cells from tobacco stem and carrot root on artificial culture medium.However,this culture failed to differentiate and grew as undifferentiated masses of parenchymatous cells called callus which could be propagated indifinitely by repeated subculturing on fresh culture medium.
Equipments used for Tissue culture:
To get success in vitro culture or micropropagation a laboratory should have following equipments and facilites.They are:
i)pH meter
i)pH meter
ii)Chemical balance
iii)Hot air oven
iv)Centrifuge
v)Auto clave
vi)UV lamp
vii)Shaker
viii)Dissecting microscope
viii)Dissecting microscope
ix)Compound microscope
x)Refrigerator
xi)Laminar air flow cabinet
xii)Essential glass
Methods of Plant Tissue Culture:
a)Nutrient Medium:
Cultured tissue can not synthesize their own food and need an external supply i.e they are heterotroph.The medium or cultured medium used in tissue culture is basal medium.It include following things:
i) Inorganic Nutrients:
It includes all the 16 elements which are essential for normal and healthy life of plants.These elements can be grouped into Macro and micro elements.
Cultured tissue can not synthesize their own food and need an external supply i.e they are heterotroph.The medium or cultured medium used in tissue culture is basal medium.It include following things:
i) Inorganic Nutrients:
It includes all the 16 elements which are essential for normal and healthy life of plants.These elements can be grouped into Macro and micro elements.
Macro elements: C,H,O,P,K,Ca,S,Mg
Micro elements :Zn,Fe,Cu,B,Mn,Mo and Cl
ii)Organic elements :
Micro elements :Zn,Fe,Cu,B,Mn,Mo and Cl
ii)Organic elements :
It includes sucrose,glucose,fructose,carbohydrats and vitamins.
iii)Natural extracts:
natural extract like yeast extract,coconut milk,tomato juice,malt extract are added in the medium.
iv)Growth Hormone:
it includes auxin,cytokinin and gibberellin
Some of the standard media available are Murasbige and Skoog's media,White's media and Nitschs media.
v)Agar:
Agar is a polysaccharide substance obtained from sea weeds which is used to provide solid surface for growth.
b)Sterilization or Aseptic Condition:
The culture must be totally free from microbian contamination.Microbes may enter culture through the ingredients of medium,througn plant organ or explant and through air so that the culture vessel and instrumenti.e glasswares,metal instruments are sterilized by exposure to hot dry air at 160 C to 170 C for 2-4 hours in a hot air oven.
i)Culture Medium:
Culture vessels containing the medium are plugged and autoclaved at 120 C for about 15-20 minutes.
ii)Plant material or Explant:
Plant material or explants are surfacesterilized by using sodium hypochloride or calcium hypochloride solution.After surfacesterilization plant materials are washed 3-4 times in a sterile distill water.
iii)Transfer Arae:
Inoculation is carried out in a laminar air flow cabinet.In this cabinet filterate sterile air flows inside at a constant rate.The flow is unidirectional and makes the cabinet sterile.
To avoid contamination hands and arms are washed with soap and then 95% ethanol.Thus an aseptic environment is maintained for tissue inoculation.
c)Light:
Normally it is not necessary for growth of culture but it plays an important role in inducing differentiation.The intensity and duration of illumination varies from species to species.
d)Temprature:
Generally 25 to 27 degree centigrade is necessary for callus growth.
e)Humidity:
A relative humidity of 70-75% is optimum for the growth of culture.
a)Shoot Culture:
Plant tissue culture in which sterile shoot tips or axillary buds are used as explants is called Shoot culture.
b)Protoplast Culture:
Here,protoplast is used as culture.Somatic hybrid can be produced from protoplast culture.
c)Embryo Culture:
The plant tissue culture in which embroyo is used as explant is known as embryo culture.
d)Anther Culture :
The plant tissue culture in which anther is used as explant is known as Anther culture.By this haploid plant is produced which is of great importance to scientist as mutation can be induced in them.
e) Meristem Culture:
The plant tissue culture in which apical meristem is taken as explant is known as meristem culture.Through this disease resistance plant can be produced.
Rapid asexual or vegetative propagation of plant in vitro is called micro propagation.Large no of plants can be produced throughout the year.
2)Somatic Hybridization:
Fusion of somatic cells in vitro is called somatic hybridisation.Novel hybrid can be produced in sexually incompatible species.
3)Production of Haploid Plants:
Through anther culture haploid plants are produced.It is very important in research point of view as mutation can be induced and detected.
4)Production of Pathogen Free Plants:
Through meristem culture,virus free plants can be produced from diseasesd material.
5)Production of Disease Resistant Varieties:
Many plants are dying due to presence of virus or bacteria.So,plant tissue culture has been able to produce disease resistance variety of plants.
6)Minimize the using space:
Tissue culture can be used to minimize the growing space in commercial nurseries for maintenance of stock plants.
Souce: http://technologysifi.blogspot.in/2010/03/plant-tissue-culture.html
natural extract like yeast extract,coconut milk,tomato juice,malt extract are added in the medium.
iv)Growth Hormone:
it includes auxin,cytokinin and gibberellin
Some of the standard media available are Murasbige and Skoog's media,White's media and Nitschs media.
v)Agar:
Agar is a polysaccharide substance obtained from sea weeds which is used to provide solid surface for growth.
b)Sterilization or Aseptic Condition:
The culture must be totally free from microbian contamination.Microbes may enter culture through the ingredients of medium,througn plant organ or explant and through air so that the culture vessel and instrumenti.e glasswares,metal instruments are sterilized by exposure to hot dry air at 160 C to 170 C for 2-4 hours in a hot air oven.
i)Culture Medium:
Culture vessels containing the medium are plugged and autoclaved at 120 C for about 15-20 minutes.
ii)Plant material or Explant:
Plant material or explants are surfacesterilized by using sodium hypochloride or calcium hypochloride solution.After surfacesterilization plant materials are washed 3-4 times in a sterile distill water.
iii)Transfer Arae:
Inoculation is carried out in a laminar air flow cabinet.In this cabinet filterate sterile air flows inside at a constant rate.The flow is unidirectional and makes the cabinet sterile.
To avoid contamination hands and arms are washed with soap and then 95% ethanol.Thus an aseptic environment is maintained for tissue inoculation.
c)Light:
Normally it is not necessary for growth of culture but it plays an important role in inducing differentiation.The intensity and duration of illumination varies from species to species.
d)Temprature:
Generally 25 to 27 degree centigrade is necessary for callus growth.
e)Humidity:
A relative humidity of 70-75% is optimum for the growth of culture.
Types of plant Tissue Culture:
Plants material used for plant tissue culture is known as explants.On the basis of explants used for plant tissue culture,it is of following type:a)Shoot Culture:
Plant tissue culture in which sterile shoot tips or axillary buds are used as explants is called Shoot culture.
b)Protoplast Culture:
Here,protoplast is used as culture.Somatic hybrid can be produced from protoplast culture.
c)Embryo Culture:
The plant tissue culture in which embroyo is used as explant is known as embryo culture.
d)Anther Culture :
The plant tissue culture in which anther is used as explant is known as Anther culture.By this haploid plant is produced which is of great importance to scientist as mutation can be induced in them.
e) Meristem Culture:
The plant tissue culture in which apical meristem is taken as explant is known as meristem culture.Through this disease resistance plant can be produced.
Applications of Plant Tissue Culture:
1)Micro propagation:Rapid asexual or vegetative propagation of plant in vitro is called micro propagation.Large no of plants can be produced throughout the year.
2)Somatic Hybridization:
Fusion of somatic cells in vitro is called somatic hybridisation.Novel hybrid can be produced in sexually incompatible species.
3)Production of Haploid Plants:
Through anther culture haploid plants are produced.It is very important in research point of view as mutation can be induced and detected.
4)Production of Pathogen Free Plants:
Through meristem culture,virus free plants can be produced from diseasesd material.
5)Production of Disease Resistant Varieties:
Many plants are dying due to presence of virus or bacteria.So,plant tissue culture has been able to produce disease resistance variety of plants.
6)Minimize the using space:
Tissue culture can be used to minimize the growing space in commercial nurseries for maintenance of stock plants.
Souce: http://technologysifi.blogspot.in/2010/03/plant-tissue-culture.html
No comments:
Post a Comment